New paper on diffusion models published in the Transactions on Machine Learning Research (TMLR) journal
We are pleased to announce that our latest research paper, "From discrete-time policies to continuous-time diffusion samplers: Asymptotic equivalences and faster training," has been published in the Transactions on Machine Learning Research (TMLR) journal.
The study addresses a significant challenge in generative AI: training diffusion models to sample from complex distributions (such as Boltzmann distributions) without the need for pre-existing target samples.
Key Contributions
Our research introduces several advancements to the field of generative modeling:
-
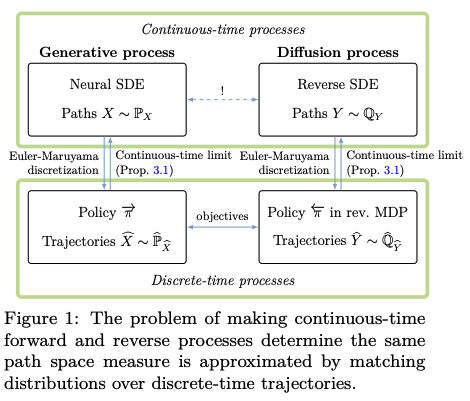
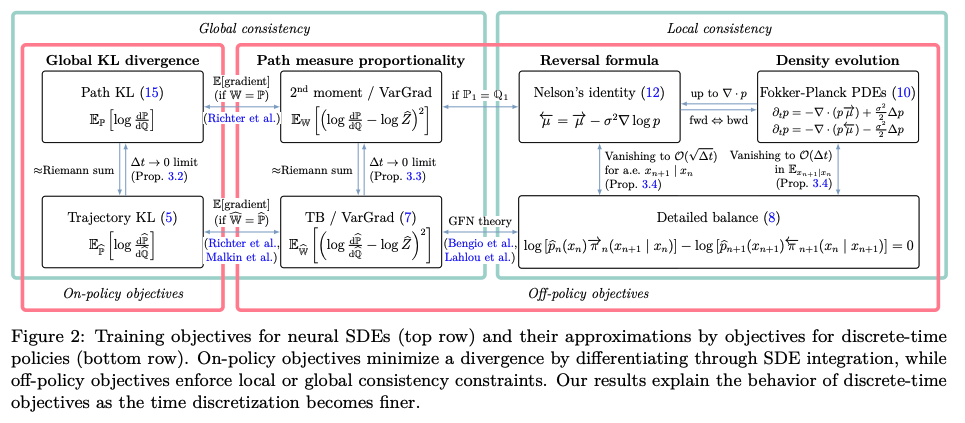
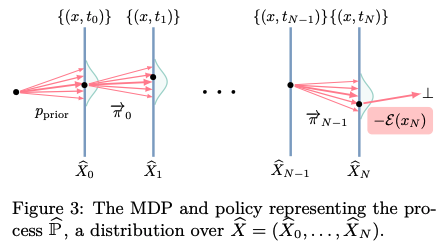
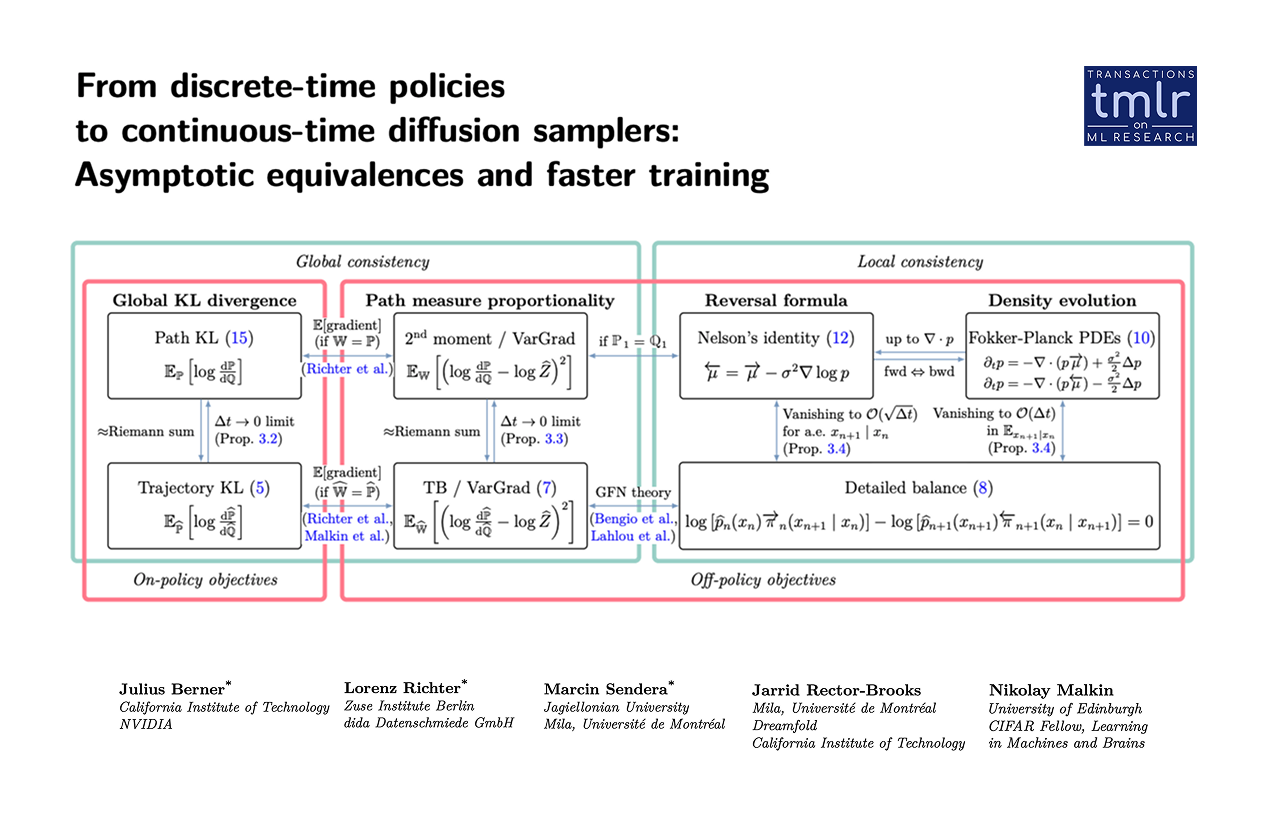
Theoretical Framework: We establish a formal mathematical bridge between discrete-time reinforcement learning (specifically GFlowNets) and continuous-time objects, including Stochastic Differential Equations (SDEs) and Partial Differential Equations (PDEs).
-
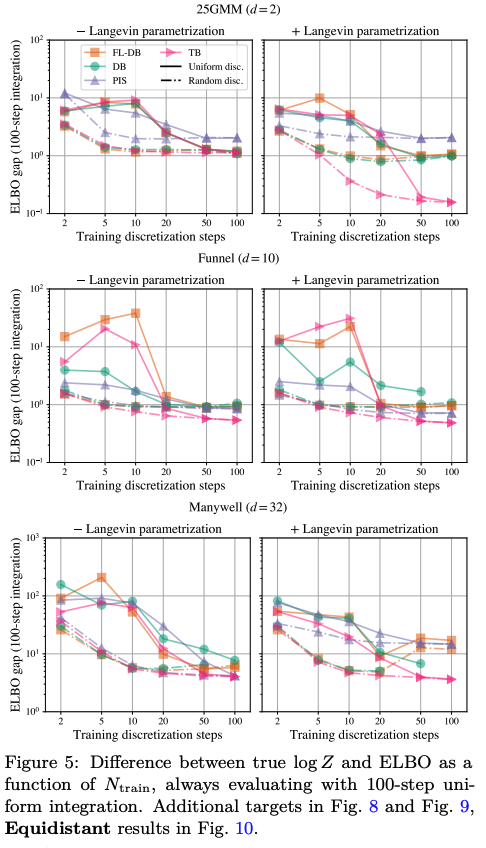
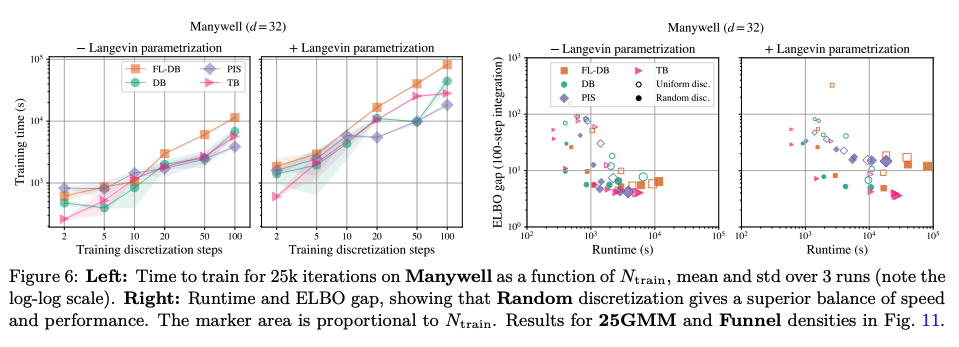
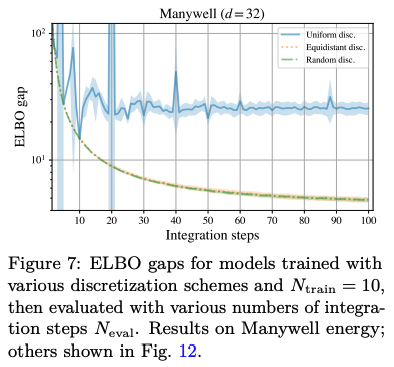
Optimization of Training: The paper demonstrates that by selecting appropriate coarse-time discretization, developers can significantly enhance sample efficiency.
-
Performance Benchmarking: Our methodology achieves faster training times and competitive performance on standard sampling benchmarks while reducing overall computational overhead.
This work reflects dida’s ongoing commitment to advancing machine learning theory to create more efficient, scalable applications for the real world.
Acknowledgments
This research was a collaborative effort. We would like to extend our gratitude to all co-authors: Julius Berner, Lorenz Richter, Marcin Sendera, Jarrid Rector-Brooks, and Nikolay Malkin.
We also thank the participating organizations for their support and resources: Caltech, NVIDIA, Jagiellonian University, Mila - Quebec Artificial Intelligence Institute, Université de Montréal, Dreamfold, The University of Edinburgh, CIFAR, and the Zuse Institute Berlin.
Resources
Here you can find the links to the paper and the journal.
Full Paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2501.06148?
Journal Information: https://jmlr.org/tmlr/